A Timeline History of Bermondsey
A timeline history of Bermondsey with prints, photographs and maps. Click on images to enlarge.
Brought to you by The Bermondsey Guide. Part of The South London Guide (est. 1999).

|
|---|
Saxon Bermondsey
The village centre was around Abbey Street. The name comes from OE and may have meant 'Beornumund's Island'. Bermondsey was a district of marshes by the Thame.
Norman Bermondsey
1082 Bermondsey Abbey founded as
a Cluniac monastery.
1086 Reference to Bermundeseye church in Domesday Book.
1127 Bermondsey Abbey given land in Dulwich and elsewhere
by Henry I.
Mediaeval Bermondsey
1154 Henry II held his court at
Bermondsey Abbey, early version of Parliament.
1392 Early mention of tanners in Bermondsey.
1450 Reference to Bermonsey.
Tudor Bermondsey
1538 Bermondsey Abbey taken by the crown.
1541 Bermondsey Abbey demolished to make Bermondsey House
in 20 acres.
Print of Bermondsey Abbey remains in 1805

1560 St Olave's Grammar School built on Tooley Street.
c. 1569 A Fete at Bermondsey, by theDutch artist, Joris Hoefnagel.
Viewpoint is the middle of today's Cluny Estate on the corner of Long lane & Bermondsey Street. St Mary Magdalen Church is to the right. Near Potters Fields there is a busy sawmill. The artist may have created an amalgam of a fete and a wedding.

1570 Elizabeth I visited Sir Thomas Pope at Bermondsey
House.
1592 Swan Theatre opened (west of Hopton Street).
Stuart Bermondsey
1667 St Mary Magdalen (prev. church for Bermondsey Abbey) rebuilt (now much altered).
Print of St Mary Magdalen in 1809

1703 Leather industry in Bermondsey granted charter by Queen Anne.
Georgian Bermondsey
1721 Guy's Hospital started by Thomas Guy (1644-1724) in St Thomas's Street.
1733 St. John, Horsleydown. Designed by Nicholas Hawksmoor (c. 1661-1736), and John James (c. 1673-1746).
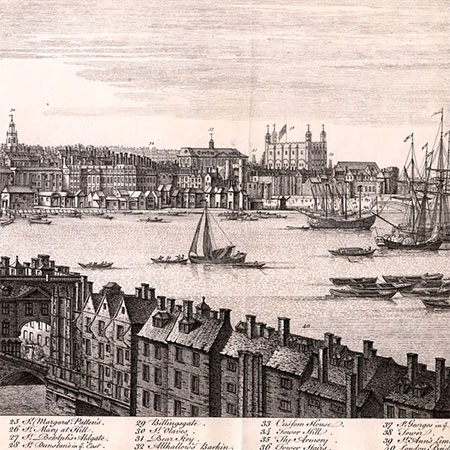
1746 Rocque's map of London.
1794 A Mr Butler, who traded in grain, rented warehouses from the Thomas family (Butlers Wharf).
1800 Southwark remained largely rural.
Regency Bermondsey
1829 St James' Church built near Jamaica Road by James Savage (1779–1852) in Classical style.
1836 First London railway started from Spa Road, Bermondsey
to Deptford.
Later linked to London Bridge.

1837 Cary's New Plan Of London And Its Vicinity map
Early Victorian Bermondsey
1839 Croydon Railway opened.
1844 Bricklayers Arms opened in Old Kent Road.
Mid Victorian Bermondsey

1866 Viaduct built above Borough Market and Clink Street
to link to Cannon Street Railway Bridge.
1867 Star Music Hall, 189 Abbey Street Bermondsey opened. Part of Star & Garter pub.
1869 Tower Subway opened (linked to Tooley Street).
1871 Stanford Library Map of London and its Suburbs
1873 Butler's Wharf, opened as a shipping wharf & warehouse complex, accommodating goods unloaded from ships using the port of London. Designed by James Tolley and Daniel Dale. All the massive Bermondsey warehouses became known as London's Larder: every variety of food, estimated to amount to three-quarters of London's imported provisions, being stored there.
1879 Bermondsey Leather & Skin Market moved to Tanner Street. Designed by George Elkington (b.1824) the new building was inscripted with words ‘The London Leather, Hide and Wool Exchange’ & included a pub. A pub still exists today, called the Leather Exchange.
Late Victorian Bermondsey
1885 New Concordia Wharf grain warehouse built by Seth Taylor as a grain warehouse. Nmed after a town called Concordia, near Kansas City, USA, from where much of the grain was imported
c. 1888 Bermondsey Vestry Hall opened. Designed by George Elkington (b.1824) in Italianate Style for the Parish of St Mary Magdalen.
1892 Bermondsey Settlement opened. it offered social, health and educational services to the local poor. Architect of the main building was Elijah Hoole (1837-1912). Demolished in 1969.

1894 Tower Bridge opened. Designed by Horace Jones (1819-1887) in collaboration with the civil engineer John Wolfe Barry (1836-1918), who devised the mechanism for the bascule bridge. Following Jones' death during the initial stages of construction, Barry completed the bridge.
Edwardian Bermondsey
1900 Metropolitan Borough of Bermondsey created.
Alfred & Ada Salter set up a general practice in Jamaica Road and moved to Bermondsey to live.
1908 Bartholomew's Atlas Of London & Suburbs
1915 Spa Road Station closed.

Pre-War Bermondsey
1921 New Southwark Bridge designed by Sir Ernest George.
1927 Photo of Star Cinema in Abbey Road(closed during WW2)

1928 St Olave¹s Church demolished.
1928 Super Cinema opened at 115 Tower Bridge Road
1920s Film of Tower Bridge market
(Manze Pie & Mash at 1:57 is still trading)
1929 Ada Salter had 9,000 trees planted, buildings decorated with window-boxes, and open spaces filled with 60,000 plants in Bermondsey.
1930 Bermondsey Town Hall opened as an extension to Bermondsey Vestry Hal on Spa Road. Designed by the Borough architect Henry Tansley in Greek Revival Style. (In 1965 Bermondsey was incorporated into Borough of Southwark. It continued as Southwark Council Offices until 2010).
1936 Bermondsey Health Centre opened on Grange Road. Designed by the Borough architect Henry Tansley. It provided infant welfare and anti-natal clinics, rooms for radiotherapy and diathermy (heat treatment using high-frequency electrical current), a foot clinic, and a solarium and dispensary for sufferers of TB. Sculpture of mother and children by Edgar Allan Howes (1888-1969).
1937 Film of Bermondsey Borough Council's new health facility in Spa Road.
WW2 Bermondsey
1940-41 Many local people killed by German bombing raids.

St. John, Horsleydown severely damaged in Blitz.
Bermondsey Vestry Hall damaged in the Blitz.
1944-5 Flying bomb attack caused extensive damage and loss of life
Post War Bermondsey
1946 Super Cinema (115 Tower Bridge Road) became Troc-ette cinema

1947 Caledonian Market moved from Islington to Bermondsey Square. It became incorporated the old Bermondsey street and Tower Bridge Road street markets. Named New Caledonia Market.

1956 Tommy Steele from Bermondsey was the first British rockers to top the UK charts

1956 Troc-ette cinema (115 Tower Bridge Road) closed.
1960 New Caledonia Market became known as Bermondsey Antique Market
1963 Star Cinema building in Abbey Street demolished
1965 Borough of Southwark was formed by amalgamation
of boroughs of Bermondsey, Camberwell and Southwark.
1968 St Olave’s School moved to Orpington from Tooley Street.
1971 Docks & wharves in Upper Port of London closed down due to containerisation.
HMS Belfast (1938), moored by Tooley Street. The largest of the WW2 cruisers, reportedly fired one of the first shots on D-Day itself.

Butlers Wharf, Shad Thames, closed as a warehouse. Rented out to artists, including Derek Jarman (1942-1994) & Andrew Logan (b. 1945). Film by Jarman. The editor attended a party there with some of the Sex Pistols. The full story.
1976 Sex Pistols played the "Valentines Day Ball", Andrew Logan's Studio, Butler's Wharf, London.
c1977 The SLG editor attended a party at Butler's Wharf with some of the Sex Pistols.
1978 X Rays Spex video filmed on roof of Butlers Wharf, Shad Thames.
1979 Artists left Butlers Wharf after an electrical fire damaged the building.
1980 Spandau Ballet played showcase on HMS Belfast film. Manager’s story.
1983 New Concordia Wharf Victorian warehouses in Mill Street converted into apartments by Waterhouse (by Andrew Wadsworth & Robert Ackland). Early Docklands conversion.
China Wharf warehouse redesigned by Piers Gough (b. 1946) of CZWG with spectacular orange red scalloped windows in Post Modern style. Grade II listed in 2018.
1989 Butlers Wharf warehouse converted into residential apartments by Conran Roche.
Design Museum opened by Terence Conran at Shad Thames. Old Victorian warehouse remodelled as a white bauhaus building. (It moved to a larger space in 2016).
The Circle by Piers Gough (b. 1946) opened along with a Shirley Pace (b. 1933) sculpture, Jacob the Dray-Horse.
1991 Le Pont De La Tour opened as the showpiece of the Butlers Wharf regeneration by Terence Conran (1931- 2020).
1993 Millwall FC moved to Senegal Fields. The new Den had 20,146 seats.
199? Part of Bermondsey Health Centre (back part including Solarium) sold off as shared-ownership flats.
1997 Bermondsey Leather & Skin Market closed on Tanner Street. Converted to work space use.
1999 Bermondsey Underground station opened as part of Jubilee Line extension between London Bridge & Canada Water. Designed by Ian Ritchie Architects Ltd.
2002 London City Hall (by Norman Foster) opened

2008 Bermondsey Square developed with a hotel, shops and a 52 seat cinema called Shortwave
2009 Southwark Council began move from Peckham Road to 100 Tooley Street
2011 White Cube Bermondsey art gallery opened on Bermondsey Street. Owned by Jay Jopling. 1970s warehouse converted into 58,000 sq ft of interior space making it, at the time, Europe's biggest commercial gallery.
2012 The Shard opened by London Bridge Station. Designed by Renzo Piano (b.1937). 72 storeys.
2022 Mayor and Assembly moved from Bermondsey to the Royal Docks.
Booklist:
The
History and Antiquities of the Parish of Bermondsey - GW Phillips (1840)
Bermondsey - ET Clarke (1901)
Bermondsey Story - F. Brockway (1949)
Old Bankside - G. Golden (1951)
Thames Crossings - G Phillips (1981).
The Story of Bermondsey - Mary Boast (1978 London Borough of Southwark)











